- [012]배열 이어서
- 배열생성과 초기화
- fill( , )함수
- main의 매개변수로 인자를 전달하는 예
- enhanced for문 (for each문)
- 로또만들기 문제
- 2차원배열
배열과 반복문은 꼭 붙어다닌다!
public class Box {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] sr = new String[7]; //7개 방을 만들어라. 참조형에서 객체생성
sr[0] = new String("Java");
sr[1] = new String("System");
sr[2] = new String("compiler");
sr[3] = new String("Park");
sr[4] = new String("Tree");
sr[5] = new String("Dinner");
sr[6] = new String("Brunch Cafe");
int cnum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < sr.length; i++)
cnum += sr[i].length();
System.out.println("총 문자의 수: " + cnum);
}
}sr 3가지 구분 무조건 하기!
sr.length 의 sr : 배열객체의 length다.
String[] sr = newString[7]; 의 sr : sr은 데이터타입이 배열
sr[0] = new String("Java"); 의 sr : sr의 데이터 타입이 String
배열 생성과 초기화

int[] arr = new int[3]은 숫자 정해줌
int arr[] = new int[3]도 가능하지만
←조금 더 선호하는 방법임
←여기와 숫자 3 안정해줘도 됨★
↑
컴파일러가 알아서 정해주기 때문
↓
←여기는 숫자 3 안정해줘도 됨★

fill( , ) 함수
import java.util.Arrays;
class Box{
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] ar1 = new int[10];
int[] ar2 = new int[10];
Arrays.fill(ar1, 7); //배열 ar1을 7로 초기화
System.arraycopy(ar1, 0, ar2, 3, 4); //배열 ar1을 ar2로 부분 복사
//ar1의 0번값을 ar2의 3번값부터 4개길이만큼 복사
for(int i =0; i<ar1.length; i++)
System.out.print(ar1[i]+" ");
System.out.println();
for(int i = 0; i<ar2.length; i++)
System.out.print(ar2[i]+" ");
}
}//결과값
7 7 7 7 7 7 7 7 7 7
0 0 0 7 7 7 7 0 0 0 fill( , ) 은 두 개의 파라미터를 요구하는 함수이다.
하나는 배열(모든 타입), 다른 하나는 해당 배열을 채울 데이터이다.
이 때 배열을 채울 데이터는 당연하지만, 배열의 데이터타입과 일치해야 한다.
String[]이 파라미터로 주어졌다면, 이 배열을 채울 데이터 또한 String이어야 한다는 이야기이다.
static키워드에 관해서 꼭 알기!!
main의 매개변수로 인자를 전달하는 예

//터미널에서 컴파일해준다음 아무값이나 넣어보기
public class Simple {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) { //무조건 외워야하는 공식
System.out.println(args[i]);
}
}
}
enhanced for(for-each) 문

←이건 오류가 날수도있긴하지만
이걸로 쓰는 연습해보기
public class Simple {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] ar = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
// 배열 요소 전체 출력
for (int e : ar) {
System.out.println(e + " ");
}
System.out.println();
int sum = 0;
//배열 요소의 전체 합 출력
for (int e : ar) {
sum += e;
}
System.out.println("sum: " + sum);
}
}
밑에 Box함수문제 응용
import java.util.Arrays;
class Simple {
private int SimpleNum;
private String season;
Simple(int sp, String season) {
this.SimpleNum = sp;
this.season = season;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Simple[] sp = new Simple[4];
sp[0] = new Simple(3, "spring");
sp[1] = new Simple(6, "summer");
sp[2] = new Simple(9, "autumm");
sp[3] = new Simple(12, "winter");
for (Simple e : sp) {
if (e.getSimpleNum() == 3)
System.out.println("봄은 영어로 " + e);
}
}
public String toString() { //toString메서드는 객체의 정보를 리턴하는 역할.
//클래스에서 toString이 override가 되어있지않으면
//Object(최상위부모)에 있는 toString을 부르게 된다
return season;
}
public int getSimpleNum() {
return SimpleNum;
}
}//봄은 영어로 spring
배열로 로또만들기 - 다시확인해보기
public class Lotto {
int[] lotto;
public Lotto() {
}
public int[] getLotto() {
int[] lotto = new int[6];
for(int i=0; i < lotto.length; i++) {
lotto[i] = (int)(Math.random() * 45) + 1;
//중복제거 구문
for(int j=0; j < i ; j++) {
if(lotto[j] == lotto[i]) {
i--; //한번 더 돌려라.
break;
}
}
}
return lotto;
}
public void getLottoNum() {
lotto = getLotto();
for(int i=0; i < lotto.length; i++) {
System.out.println(lotto[i]);
}
}
}public class LottoMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 로또번호 1-45, 6개, 중복없이.
//중복제거는 이전에올려놨던 메모리 비교해서 같으면 제거.
System.out.println("로또 번호");
Lotto lotto = new Lotto();
lotto.numRandom();
}
}
2차원배열
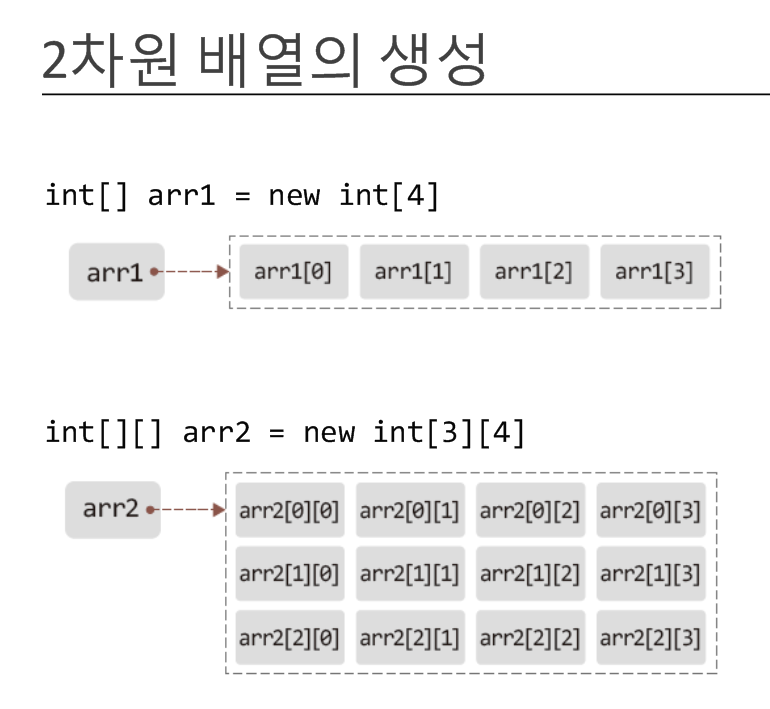
class Box {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] arr = new int[3][4];
int num = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++) {
arr[i][j] = num;
num++;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++) {
System.out.println(arr[i][j] + "\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}//결과값
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
2차원 배열

↓무조건 외우기
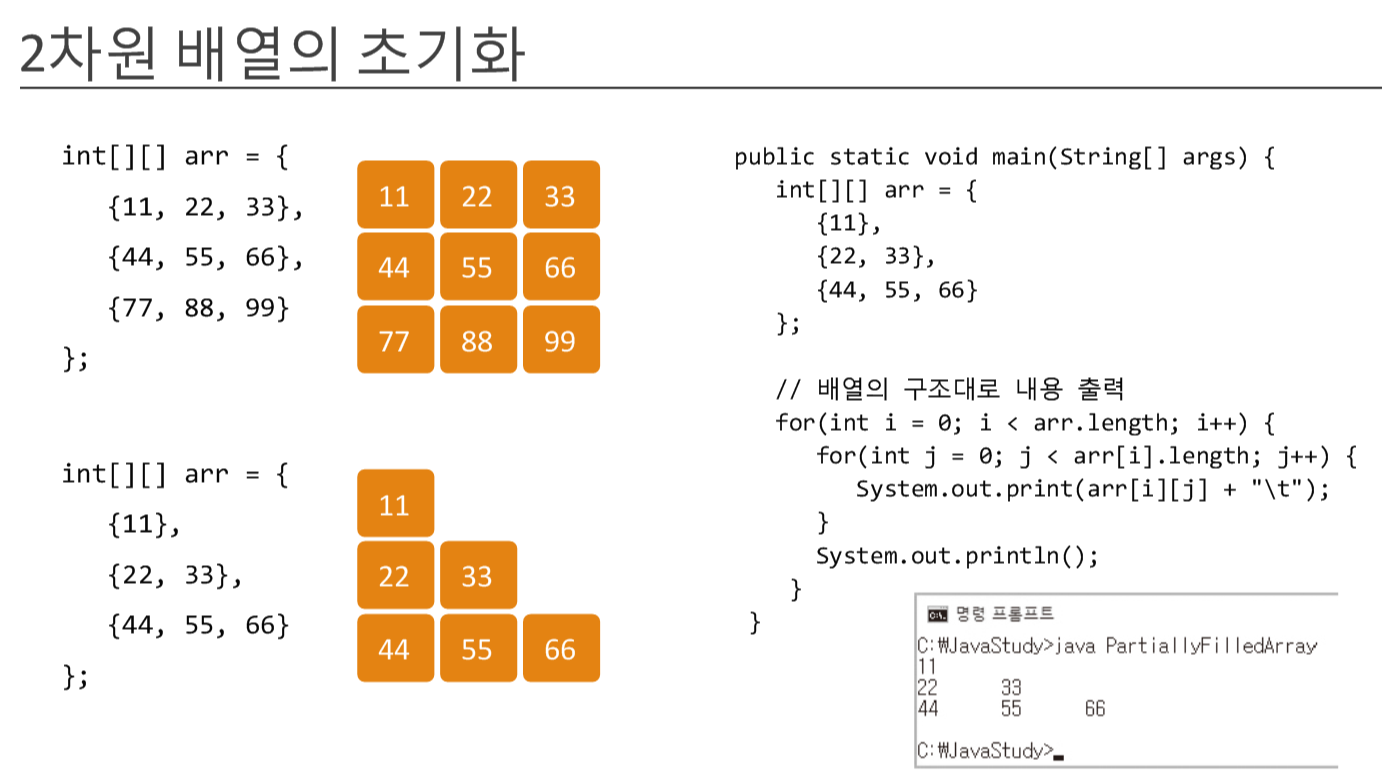
arr.length = 행 (3개)
arr[i].length =
class Box {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] arr = {
{ 11 },
{ 22, 33 },
{ 44, 55, 66 } };
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < arr[i].length; j++) {
System.out.print(arr[i][j] + "\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
//11
//22 33
//44 55 66오늘의 문제
1.배열의 디폴트 초기화 방법은?
①int[] arr = new int[3]
②int[] arr = new int[] {1,2,3};
③int[] arr = {1,2,3};
int arr[] = new int[3]도 가능하지만
①이 조금 더 선호하는 방법이다.
②③은 컴파일러가 알아서 정해준다.
2.arraycopy 함수의 사용 방법은?
ex. System.arraycopy(ar1, 0, ar2, 3, 4); //배열 ar1을 ar2로 부분 복사
//ar1의 0번값을 ar2의 3번값부터 4개길이만큼 복사
3.public static void main(String[] args) 에서 String[] args 의 사용법과 용도는?
프로그램 실행시 맥변수를 보내서 실행할 수 있다는 것이다.
클래스 이름 뒤에 값을 주게 되면 공백을 기준으로 문자열을 잘라서 배열에 담아 main() 메서드의 파라미터 값으로 넘어온다

4.enhenced for 문에 대하여 설명하시오.
강화된 for문, for-each
배열 각각의 요소에 순차적으로 접근함
기존 for문보다 간편 해짐: 코드의 양이 줄고 배열의 길이와 요소에 신경 쓸 필요가 없다.
5.로또 프로그램을 작성하시오.
LottoMain.java
//로또번호 :랜덤번호 1-45, 6개, 중복없이
public class LottoMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Lotto lottoGame = new Lotto();
lottoGame.showRandomN();
}
}Lotto.java
public class Lotto {
private int[] lottoNum;
public Lotto() {
}
private int[] getRandomN() {
int[] ranNum = new int[6]; // 6개 로또 수 만들기
for (int i = 0; i < ranNum.length; i++) {
ranNum[i] = (int) (Math.random() * 45) + 1;
for (int j = 0; j < ranNum.length; j++) {
if (ranNum[i] == ranNum[j])
break;
}
}
return ranNum;
}
public void showRandomN() {
lottoNum = getRandomN();
for (int i = 0; i < lottoNum.length; i++) {
System.out.print((lottoNum[i] + " "));
}
}
}
6.아래의 프로그램을 참고 하여 Box class 를 짜시오.
class Box {
private int SimpleNum;
private String word;
Box(int sp, String word) {
this.SimpleNum = sp;
this.word = word;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Box[] ar = new Box[5];
ar[0] = new Box(101, "Coffee");
ar[1] = new Box(202, "Computer");
ar[2] = new Box(303, "Apple");
ar[3] = new Box(404, "Dress");
ar[4] = new Box(505, "Fairy-tale book");
for (Box e : ar) {
if (e.getSimpleNum() == 505)
System.out.println(e);
}
}
public String toString() {
return word;
}
public int getSimpleNum() {
return SimpleNum;
}
}
7.양의 정수 10개를 랜덤생성하여, 배열에 저장하고, 배열에 있는 정수 중에서 3의 배수만 출력해보자.
package java_1209_prac;
public class ThreeMulti {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] num = new int[10];
for (int i = 0; i < num.length; i++) {
num[i] = (int) ((Math.random() * 10) + 1);
}
for (int i = 0; i < num.length; i++) {
if (num[i] == 0)
continue;
if (num[i] % 3 == 0) {
System.out.print(num[i] + " ");
}
}
}
}
8.아래의 프로그램을 짜시오.(필수)
-5개의 숫자를 랜덤으로 받아 배열로 저장
-5개의 숫자중 가장 큰값을 출력
import java.util.Scanner;
public class NumberMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int i;
int[] num = new int[5];
System.out.println("숫자 5개 입력");
int max = num[0];
for (i = 0; i < num.length; i++) {
num[i] = sc.nextInt();
}
for (int j : num) {
System.out.println(j);
}
for (i = 0; i < num.length; i++) {
if (max < num[i]) {
max = num[i];
}
}
System.out.println("가장 큰 값은? " + max);
}
}
package java_1209_prac;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Number {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] num = new int[5];
System.out.println("숫자 5개 랜덤 출력");
int max = num[0];
for (int i = 0; i < num.length; i++) {
num[i] = (int) (Math.random() * 100) + 1;
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
if (num[i] == num[j])
i--;
break;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < num.length; i++) {
if (max < num[i]) {
max = num[i];
}
System.out.print(num[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println("\n가장 큰 값은? " + max);
}
}
9.아래의 프로그램을 짜시오.
-5개의 숫자를 랜덤으로 받아 배열로 저장
-5개의 숫자를 내림차순으로 정렬하여 출력
버블솔트,퀵솔트 영상보기 - 면접에 무조건 나오고 실무에 무조건쓰임
www.youtube.com/watch?v=lyZQPjUT5B4
www.youtube.com/watch?v=ywWBy6J5gz8
public class Array {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int sixsu[] = new int[5]; // int형 배열 선언
// 6개의 숫자 입력
System.out.println("5개의 숫자");
for (int i = 0; i < su.length; i++) {
su[i] = (int) (Math.random() * 100) + 1;
}
// 입력한 값 출력
System.out.print("입력된 값은 : ");
for (int j = 0; j < 6; j++) {
System.out.print(su[j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
// 입력받은 수를 큰 순서대로 넣기
for (int i = 0; i < su.length; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < su.length; j++) {
if (su[i] < su[j]) {
int temp = su[i]; //temp는 최댓값 넣는곳.
su[i] = su[j]; //i를 j에 넣어주기
su[j] = temp;//temp를 j에 넣기
}
}
}
// 결과값 출력
System.out.print("큰 수부터 출력 : ");
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
System.out.print(su[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}↓선생님코드
class ArrAvg {
final int ROWS = 10;
int[] numArr;
ArrAvg() {
numArr = new int[ROWS];
}
private void input() {
for (int i = 0; i < numArr.length; i++) {
numArr[i] = (int) (Math.random() * 10) + 1;
}
}
private void output() {
double avg = 0;
double total = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < numArr.length; i++) {
total = total + numArr[i];
System.out.print(numArr[i] + " ");
}
avg = total / numArr.length;
System.out.println();
System.out.println(avg);
}
public void getResult() {
input();
output();
}
}
class ArrUtils {
public static void bubleSort(int[] arr) {
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < arr.length - i - 1; j++) {
if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1]) {
int temp = arr[j + 1];
arr[j + 1] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
}
}
}
public static int maxArr(int[] arr) {//static 넣기!!
if (arr == null) {
System.out.println("배열이 없습니다.");
return -1;
}
int max = arr[0]; //int에 최솟값 넣어주기
for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (max < arr[i]) {
max = arr[i];
}
}
return max;
}
} //메인함수 폴더명 DescendingOrderMain
public class DescendingOrderMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = new int[10];
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
arr[i] = (int) (Math.random() * 100) + 1;
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
int max = ArrUtils.maxArr(arr);
ArrUtils.bubleSort(arr);
for (int i : arr) {
System.out.print(i + " ");
}
}
}
10. char 배열을 생성하여, 알파벳 A~Z까지 대입 후, 출력해보자. 알파벳은 26개.
public class Array {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//char[] alphabet = new char[26];
for (int num = 65; num <= 90; num++) {
for(int i = 0; i < 26; i++)
char[] alphabet = new char[i];
}
}
}
10.배열과 반복문을 이용하여 프로그램을 하시오. 키보드에서 정수로 된 돈의 액수를 입력받아 오만 원권, 만 원권, 천 원권, 500원짜리 동전, 100원짜리 동전, 50원짜리 동전, 10원짜리 동전, 1원짜리 동전이 각 몇 개로 변환되는지 예시와 같이 출력하라. 이때 반드시 다음 배열을 이용하고 반복문으로 작성하라.
int[] unit = {50000, 10000, 1000, 500, 100, 50, 10, 1}; // 환산할 돈의 종류
금액을 입력하시오 >> 65123
50000 원 짜리 : 1개
10000 원 짜리 : 1개
1000 원 짜리 : 5개
500 원 짜리 : 0개
100 원 짜리 : 1개
50 원 짜리 : 0개
10 원 짜리 : 2개
1 원 짜리 : 3개
12.정수를 10개 저장하는 배열을 만들고 1에서 10까지 범위의 정수를 랜덤하게 생성하여 배열에 저장하라. 그리고 배열에 든 숫자들과 평균을 출력하라.(필수)
랜덤한 정수들 : 3 6 3 6 1 3 8 9 6 9
평균은 5.4
내코드↓
public class Array {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double sum = 0;
int[] num = new int[10];// 배열생성
System.out.println("랜덤한 정수들 : ");
for (int i = 0; i < num.length; i++) {
num[i] = (int) (Math.random() * 10) + 1;
sum += num[i];
System.out.print(num[i] + " ");
} // 랜덤값&합계
System.out.print("\n평균 : " + sum / num.length);
}
}
선생님코드↓
import java.util.Random;
public class AvgNum {
private int[] num;
private final int ROWS;
public AvgNum() {
ROWS = 10;
num = new int[ROWS];
}
public int[] getNum() {
return num;
}
public void setNum(int[] num) {
this.num = num;
}
private void rndNum() {
Random random = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < num.length; i++) {
num[i] = random.nextInt(10) + 1;
}
}
private double rndNumAvg() {
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < num.length; i++) {
sum += num[i];
}
return (double)sum / num.length;
}
public void user() {
rndNum(); //이거 안넣어주면 배열 0만 나옴
System.out.print("랜덤한 정수들 : ");
for (int i = 0; i < num.length; i++) {
System.out.print(num[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
//sumaverNum(); //얘는 왜 안넣어줘도되는지?
System.out.println("평균은 " + rndNumAvg());
}
}public class AvgNumMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AvgNum avgNum = new AvgNum();
avgNum.user();
}
}
13. 4 x 4의 2차원 배열을 만들고 이곳에 1에서 10까지 범위의 정수를 랜덤하게 생성하여 정수 16개를 배열에 저장하고, 2차원 배열을 화면에 출력하라.(필수)
8 6 1 1
7 3 6 9
4 5 3 7
9 6 3 1
public class ArayRandom {
// .4 x 4의 2차원 배열을 만들고 이곳에 1에서 10까지 범위의
// 정수를 랜덤하게 생성하여 정수 16개를 배열에 저장하고,
// 2차원 배열을 화면에 출력하라.(필수)
//
// 8 6 1 1
// 7 3 6 9
// 4 5 3 7
// 9 6 3 1
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] num = new int[4][4]; //// 다이렉트로[4][4]할순있지만 좋은게x
for (int i = 0; i < num.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < num[i].length; j++) {
num[i][j] = (int) (Math.random() * 10) + 1;
System.out.print(num[i][j] + "\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}선생님 답
public class RecMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] num = new int[4][4];
for (int i = 0; i < num.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < num[i].length; j++) {
num[i][j] = (int) (Math.random() * 10) + 1;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < num.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < num[i].length; j++) {
System.out.print(num[i][j]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
↓클래스로 구현하기
class TwoArr {
// int[][] num = new int[4][4];그냥 이렇게 해도 좋지만
// 생성자의 진짜 역할 초기화를 제대로 해주기위해 밑에 코딩으로!
final int ROWS = 4;
final int COLS = 4; // 중요!!!
int[][] num;
TwoArr() {
num = new int[ROWS][COLS]; // 다이렉트로[4][4]할순있지만 좋은게x
}
public void input() {
for (int i = 0; i < num.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < num[i].length; j++) {
num[i][j] = (int) (Math.random() * 10) + 1;
}
}
}
public void output() {
for (int i = 0; i < num.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < num[i].length; j++) {
System.out.print(num[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public void comp() {
input();
output();
}
}
package java_1210;
public class RecMain2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] num = new int[4][4];
TwoArr two = new TwoArr();
two.comp();
}
}
14.아래를 메모리 구조로 표현하시오.
int[][] arr = new int[3][4]

1행을 담고있는 주소
arr[0]ㅁ→ | [00] | [01] | [02] | [03] |
arr[1]ㅁ→ | [10] | [11] | [12] | [13] |
arr[2]ㅁ→ | [20] | [21] | [22] | [23] |
'코딩 > 수업 정리' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 20.12.11 Fri [015] (0) | 2020.12.11 |
|---|---|
| 20.12.10 Thu [014] (0) | 2020.12.10 |
| 20.12.08 Tue [012] (0) | 2020.12.08 |
| 20.12.07 Mon [011] (0) | 2020.12.07 |
| 20.12.04 Fri [010] (0) | 2020.12.04 |




댓글