- static
- static 초기화 블록
- 메소드 오버로딩
- 키워드 this
- string 클래스
- 오늘의 문제
**기본 용어상식 : 메소드 = 클래스함수

//인스턴스변수는 static하고 연관지을수가 없다.-에러나니까
static함수(클래스메소드)안에 인스턴스변수,인스턴스함수가 올 수 없는 이유는?
같은클래스내에서 static은 static끼리 놀아야한다.(static클래스, static메소드)
public class AAA {
int num = 0; //인스턴스 함수
static void addNum(int n) { //static 함수,클래스메소드
num += n; //인스턴스 함수 오면 오류
}
}public class java_area {
public class GradMain{
int num2;//인스턴스변수 - 오류없애려면 static int num2;
public static void main(String[] args) {
int num; //지역변수
num2= 0;
}
}
}
static 초기화 블록 - 프로그래밍하다보면 가끔보임
static{ }
public class DateOfExecution {
static String date; //프로그램 날짜 저장하기 위한 변수
//↓인스턴스 생성과 관계 없이 static 변수가 메모리 공간에 할당될 때 실행이 된다.
static { //이부분이 없으면 null값나옴
LocalDate nDate = LocalDate.now();
date = nDate.toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(date);
}
}
메소드 오버로딩
: println 이 대표적 예

컴파일이 된다는것은 뭔가가 다르기때문이다.
1)파라미터의 갯수를 달리한다.
2)데이터 타입을 다르게한다(변수이름 같아도 상관x)
함수 오버로딩이란? (면접 100%)
같은 함수이름으로 매개변수(파라미터)의 갯수를 달리하거나 데이터 타입을 달리해서 만들 수 있는 것(쓸 수 있는 것) - c언어에서는 불가능함
System.out.println(3.14);
System.out.println('가');
System.out.println("하이");
System.out.println(7);
System.out.println();
//println은 함수 오버로딩의 대표적인 예
class Person {
private int regiNum; // 주민번호 / private 까먹지 말기
private int passNum; // 여권번호
Person(int rnum, int pnum) {
regiNum = rnum;
passNum = pnum;
}
Person(int rnum) {
regiNum = rnum;
passNum = 0;
//this (rnum, 0); 위에 두개 대신 이걸 써도 가능!
//why? 생성자를 호출하기 때문에!
}
void showPersonalInfo() {
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person jung = new Person(335577, 112233);// 여권있는사람
Person hong = new Person(775544);// 여권없는사람
//생성자 오버로딩을 통해 두개의 유형을 구분할 수 있다.
jung.showPersonalInfo();
hong.showPersonalInfo();
}
}
키워드 this
this. - .은 함수
this는 객체. 자기자신

string 클래스
- length함수
.length → 문자열의 갯수 (띄어쓰기도 갯수로 포함!)
public class prac {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = new String("Simple String");
String str2 = "The Best String";
System.out.println(str1.length());
System.out.println(str2.length());
}
}//13
//15public class prac {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = new String("Simple String");
String str2 = "The Best String";
System.out.println(str1);
System.out.println(str1.length());
System.out.println(); //'개 행'
System.out.println(str2);
System.out.println(str2.length());
System.out.println(); //'개 행'
showString("Funny String");
}
public static void showString(String str) {
System.out.println(str);
System.out.println(str.length());
}
}//Simple String
//13
//The Best String
//15
//Funny String
//12
** 기본 상식 : char는 왜2byte? → 유니코드여서
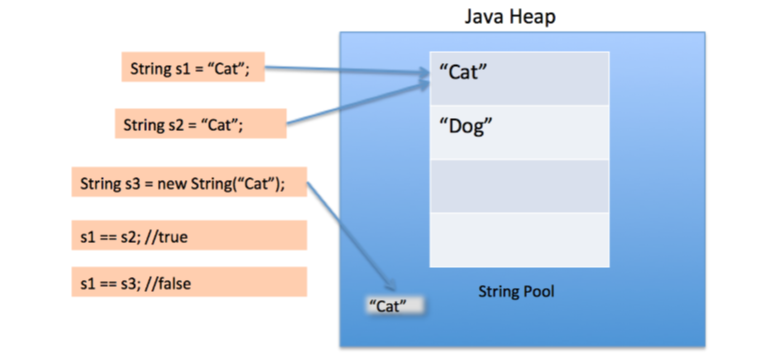
String연산은 새로운 객체를 계속 만들어내기 때문에 메모리관리가 비효율적임
그래서 만들어진 메모리영역이 "String Constant Pool".
ex) String str1 = "Simple String" →문자열 함수. ""는 안에 들어가는 문자는 대소문자 다 따져서 instance pool에 객체가 만들어진다. 만약 str2처럼 두개다 똑같으면 한개만 올린다. 동일 인스턴스임.
str3이랑 str4는 Heap메모리에 개별객체가 만들어진다.
string인스터스는 대표적인 immutable인스턴스이다.

zimt.tk/201207_-_011_ststic-String-1e0dff1e908346a3a1aadf037a1733ce
오늘의 문제
1.인스턴스 함수안에 스태틱 변수와 함수가 올수 있는 이유는?
인스턴스함수가 존재한다는 것은 이미 클래스함수가 있다는 뜻이기 때문이다.
2.메소드 오버로딩이란?
같은 함수이름으로 매개변수(파라미터)의 갯수를 달리하거나 데이터 타입을 달리해서 만들 수 있는 것(쓸 수 있는 것) - c언어에서는 불가능하다.
3.메소드 오버로딩을 적용한 대표적인 함수는?
println
4.this 함수에 대하여 설명하시오.
생성자를 호출하는것. (다이렉트로 호출을 못하니까 this를 쓰는것)
this( ); //생성자 함수: this 생성자라고 표현
this.뒤에오는변수는 인스턴스변수이다.
인스턴스 변수와 파라미터 이름이 같을 때 구분하기 위해 사용
5. this란 무엇인가?
객체. 자기자신이다.
6.스트링 객체를 생성하는 2가지 방법은?
.아래의 결과를 예측하고,이유를 설명하시오.
String str1 = "Simple String";
String str2 = "Simple String";
String str3 = new String("Simple String");
String str4 = new String("Simple String");
if(str1 == str2)
System.out.println("str1과 str2는 동일 인스턴스 참조");
else
System.out.println("str1과 str2는 다른 인스턴스 참조");
if(str3 == str4)
System.out.println("str3과 str4는 동일 인스턴스 참조");
else
System.out.println("str3과 str4는 다른 인스턴스 참조");
//예측
//str1과 str2는 동일 인스턴스 참조.
//str3과 str4는 다른 인스턴스 참조.
-이유: ""을 그대로 받은 함수는 instance pool에 객체가 만들어진다(대소문자 다 따짐). st1, str2처럼 두개 다 똑같으면 메모리를 한개만 올린다.
str3,st4는 각각 새로운 객체생성을 했기때문에 서로 다른 인스턴스이다.
7.immutable 에 대하여 설명하시오.
불변하는 인스턴스라는 뜻이다.
8. 사용자로부터 받은 문자열(영문으로)에서 자음과 모음 개수를 계산하는 프로그램을 작성하라.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class prac {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//오류 - String alpha에 들어있는 모음을 num값이 읽어내지 못한다.
int num = 0;// 모음값더하기
int i = 0;// 문자열갯수 초기화
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String alpha = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("입력한 문자열 갯수 : " + alpha.length());
i = alpha.length();// 문자열갯수 초기화
switch (alpha) {
case "a":
num++;
case "e":
num++;
case "i":
num++;
case "o":
num++;
case "u":
num++;
}
System.out.println("모음갯수 : " + (i - num));
}
}
9. 사용자로부터 키를 입력받아서 표준 체중을 계산한 후에 사용자의 체중과 비교하여 저체중인지, 표준인지, 과체중인지를 판단하는 프로그램을 작성하라. 표준 체중 계산식은 다음을 사용하라.
표준체중 = ( 키 - 100 ) * 0.9
import java.util.Scanner;
public class prac {
private static int a = 1;
private static int b = 2;
private static int c = 3;
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("키를 입력하세요.");
Scanner sc1 = new Scanner(System.in);
double height = sc1.nextInt();
double Height = (height-100)*0.9;
System.out.println(Height+"kg보다 몸무게가 1.적게 나간다 2.많이 나간다 3.동일하다");
Scanner sc2 = new Scanner(System.in);
int num = sc2.nextInt();
if(num == a) {
System.out.println("저체중입니다");
}else if(num == b) {
System.out.println("과체중입니다");
}else if(num ==c){
System.out.println("표준체중입니다");
}
}
}
10. 2와 100 사이에 있는 모든 소수(prime number)를 찾는 프로그램을 작성하라. 주어진 정수 k를 2부터 k-1까지의 숫자로 나누어서 나머지가 0인 것이 하나라도 있으면 소수가 아니다.
public class prac {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 2; // i : 나눌 대상
int num = 100;
boolean Prime = true;
while (i <= num) {
Prime = true;
for (int n = 2; n < i; n++) {
if (i % n == 0) {
Prime = false;
break;
}
continue;
}
if (Prime == true)
System.out.println(i);
i++;
}
}
}
11.사용자에게 받은 문자열을 역순으로 화면에 출력하는 프로그램을 작성하시오.
입력:abcde
출력:edcba
public class prac {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//오류 - 문자열을 5개밖에 입력못하고 입력할때마다 엔터를 쳐줘야 원하는 결과값이 나온다.
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String a = sc.nextLine();
String b = sc.nextLine();
String c = sc.nextLine();
String d = sc.nextLine();
String e = sc.nextLine();
System.out.print(e+d+c+b+a);
}
}↓정답코드
package java_1207;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Reverse {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String words;
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
words = sc.nextLine(); // words = sc.next로 해도 상관x -두개는 다른거긴함
for (int i = words.length() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
System.out.print(words.charAt(i));// char값으로 반대로 출력
}
}
}
객체생성해서 만드는 코드
//과정 - private 넣어주고 Reverse따로 만들어준뒤 this.함수만들기
package java_1208;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Reverse {
private String words;
public Reverse(String words) {
this.words = words;
}
}//과정 - getter,setter함수 만들기
package java_1208;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Reverse {
private String words;
public Reverse(String words) {
this.setWords(words);
}
public String getWords() {
return words;
}
public void setWords(String words) {
this.words = words;
}
}
//객체생성으로 만든 코드-완성본
package java_1208;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Reverse {
private String words;
public Reverse(String words) {
this.setWords(words);
}
public Reverse() { //디폴트 생성자 없을시 생기는 문제점
// https://cloudstudying.kr/questions/370 블로그확인
//super와 부모,자식클래스 추가 설명 https://jwdeveloper.tistory.com/8
}
public void input() {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("입력할 단어를 넣으세요");
words = sc.next();
sc.close();
}
public void reversePrint() {
if (words == null) { // null체크부터 해주기!!
System.out.println("단어 입력이 안되어있습니다.");
return;
} else {
for (int i = words.length() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
System.out.print(words.charAt(i));
}
}
// public void print() { //???
// input();
// reversePrint();
// }
}
public String getWords() {
return words;
}
public void setWords(String words) {
this.words = words;
}
}package java_1208;
public class ReverseMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Reverse reverse = new Reverse();
reverse.input();
reverse.reversePrint();
}
}'코딩 > 수업 정리' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 20.12.09 Wed [013] (0) | 2020.12.09 |
|---|---|
| 20.12.08 Tue [012] (0) | 2020.12.08 |
| 20.12.04 Fri [010] (0) | 2020.12.04 |
| 20.12.03 Thu [009] (0) | 2020.12.03 |
| 20.12.02 Wed [008] (0) | 2020.12.02 |




댓글